 Business Analytics
Business Analytics
Data Analytics
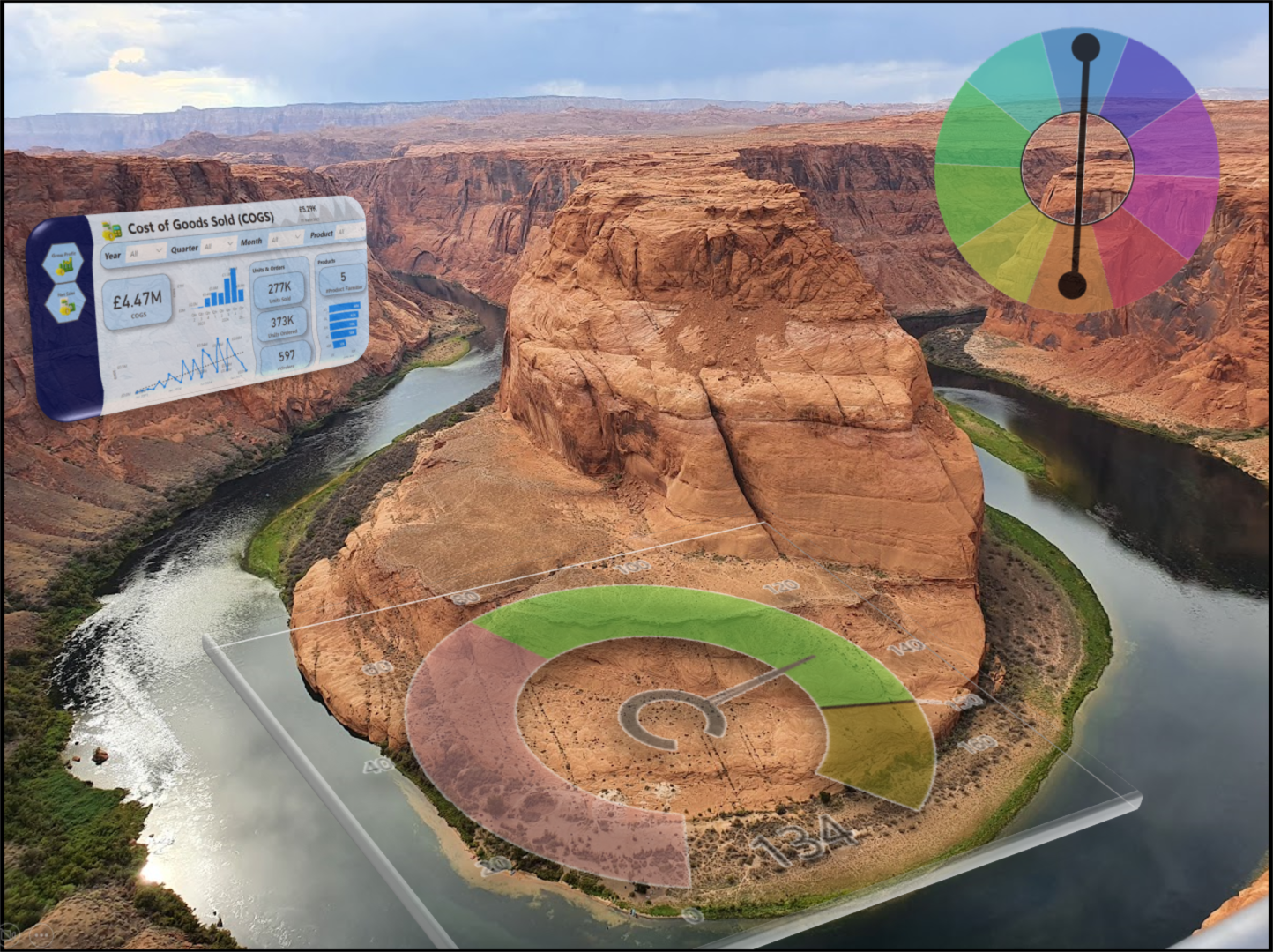

Data Analytics is the discipline of extracting actionable insights by structuring, processing, analysing and visualising data using methods and software tools.
Benefits
- Improved decision-making
- Enhanced data-driven strategies
- Better understanding of customer behaviour
Applications
- Market research and segmentation
- Financial analysis
- Customer retention
Examples
For example, a retail company may use data analytics to analyse sales data and identify trends, helping them optimise inventory and pricing strategies.
Book and Tutorials
- Data Analytics for Business: This book contains material about AI, Machine Learning, Power BI, SQL and R. Additionally, many data sets are provided.
- Tutorial: Learn to become a Data Analyst - free interactive tutorials.
Operational Analytics
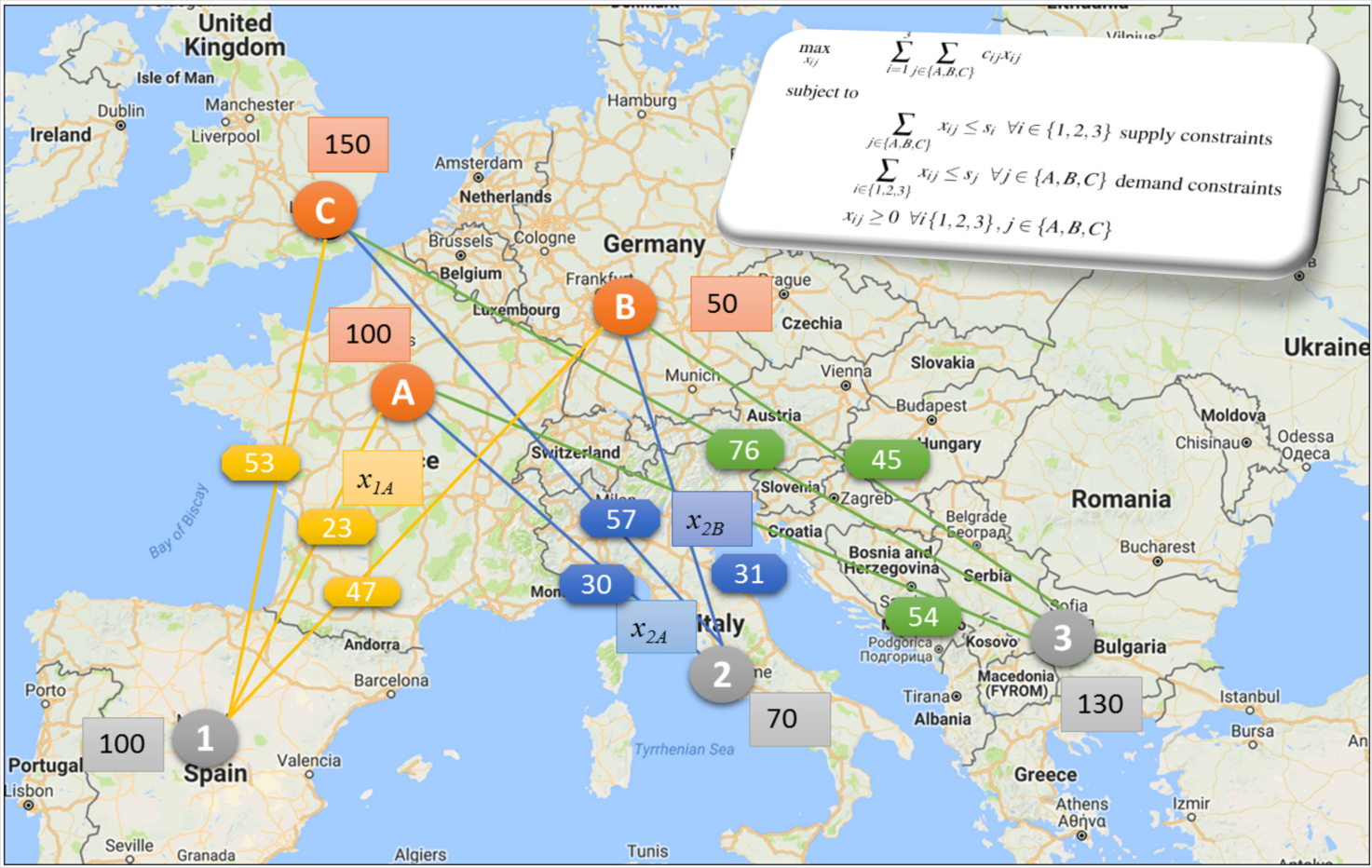
Operational Analytics not only uses data and analytics to improve day-to-day operations within an organisation, leading to more efficient processes, but finds the best solutions for the business.
Benefits
- Increased operational efficiency
- Optimal cost reduction
- Real-time monitoring
Applications
- Supply chain optimisation
- Quality control
- Inventory management
Examples
For instance, a manufacturing company may use operational analytics to find the optimal production strategy, monitors production lines and detect anomalies, reducing changeovers and improving product's profit & quality.
Book and Tutorials
- Introduction to Management Science: This book contains material about Modelling, Optimisation and Probability. It has several related YouTube tutorials.
- Math Programming App: This online app has many operational research optimisation examples.
Business Analytics

Business Analytics combines data analysis and statistical techniques to help businesses make data-driven decisions and gain a competitive advantage.
Benefits
- Competitive intelligence
- Improved profitability
- Optimised marketing campaigns
Applications
- Predictive analytics
- Customer segmentation
- Performance forecasting
Examples
For example, an e-commerce company may use business analytics to analyse customer data and create personalised product recommendations, increasing sales and customer satisfaction.
Bus Analytics

Bus Analytics combines data analysis and statistical techniques to help bus companies make data-driven decisions and gain a competitive advantage.
Benefits
- Increased in passenger journeys
- Improved services
- Insights about passengers
Applications
- Predictive analytics
- Customer segmentation
- Performance forecasting
Examples
For example, an bus service provider seeks to create a bus route that maxmimises its profit. Another example: A council wants to improve its enviromental impact by offering an attractive public transport solution.